算法基础篇(10)递归型枚举与回溯剪枝
本文介绍了搜索算法的基本概念与实现方法。搜索是通过枚举所有可能情况来寻找最优解或统计合法解,主要包括深度优先搜索(DFS)和宽度优先搜索(BFS)。文中重点讲解了四种枚举问题的DFS实现:子集枚举通过递归构建选择路径,组合枚举按顺序选择元素,排列枚举使用标记数组避免重复,全排列则输出所有可能的排列。每个算法都包含回溯过程,即撤销选择以恢复现场。这些方法为解决问题提供了系统的枚举框架,适用于各种组合
·
搜索,是一种枚举,通过穷举所有情况来找到最优解或者统计合法解的个数。搜索一般分为深度优先搜索(DFS)与 宽度优先搜索(BFS)
回溯:在搜索过程中,遇到走不通或者走到底的情况,就回头
剪枝:剪掉在搜索过程中重复出现或者不是最优解的分支
1、枚举子集
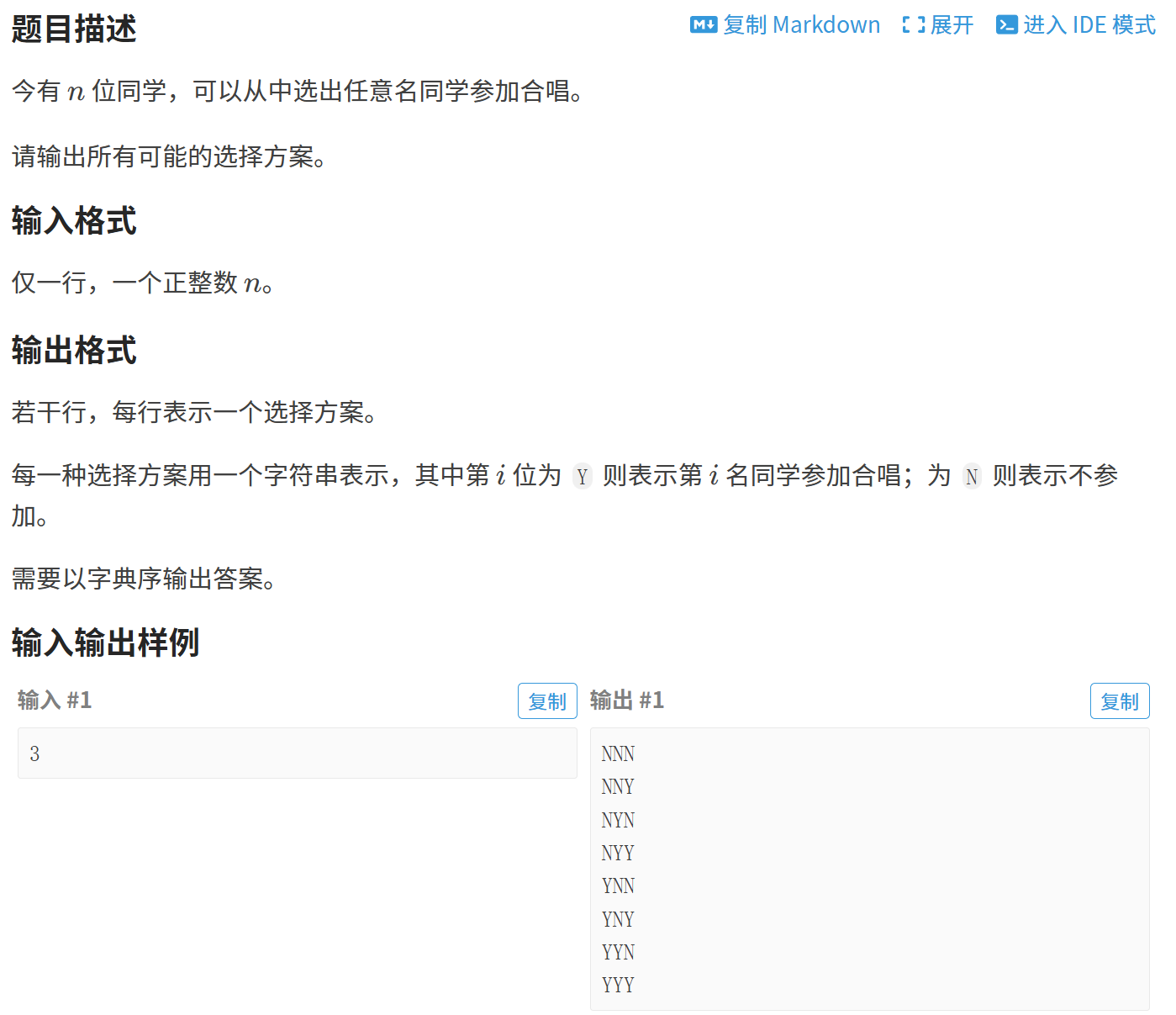
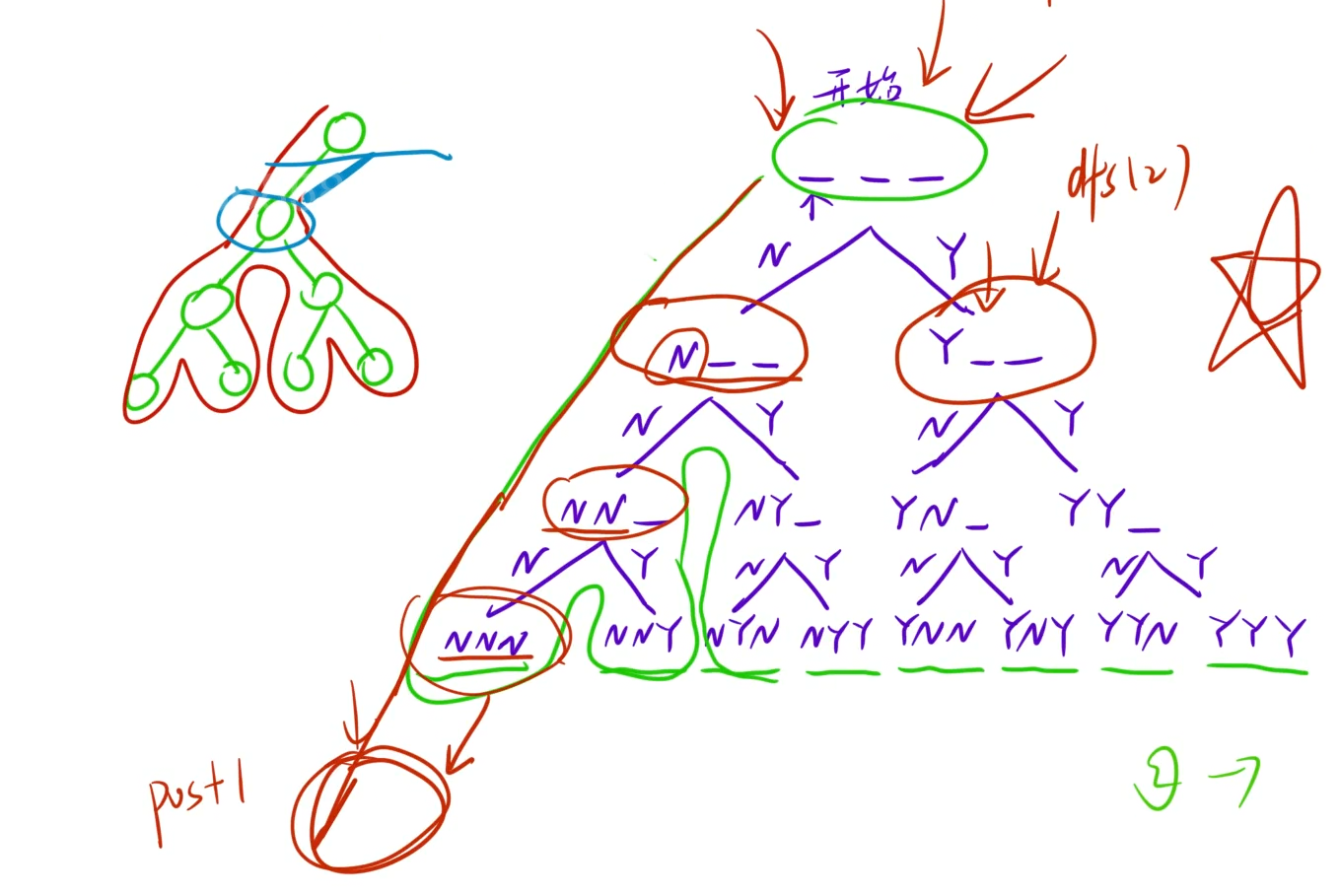
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
string path; //记录递归过程中,每一步的决策
void dfs(int pos)
{
if (pos > n)
{
//path存着前n个人的决策
cout << path << endl;
return;
}
//不选
path += "N";
dfs(pos + 1);
path.pop_back(); //回溯,清空现场
//选
path += "Y";
dfs(pos + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}1.2 组合型枚举
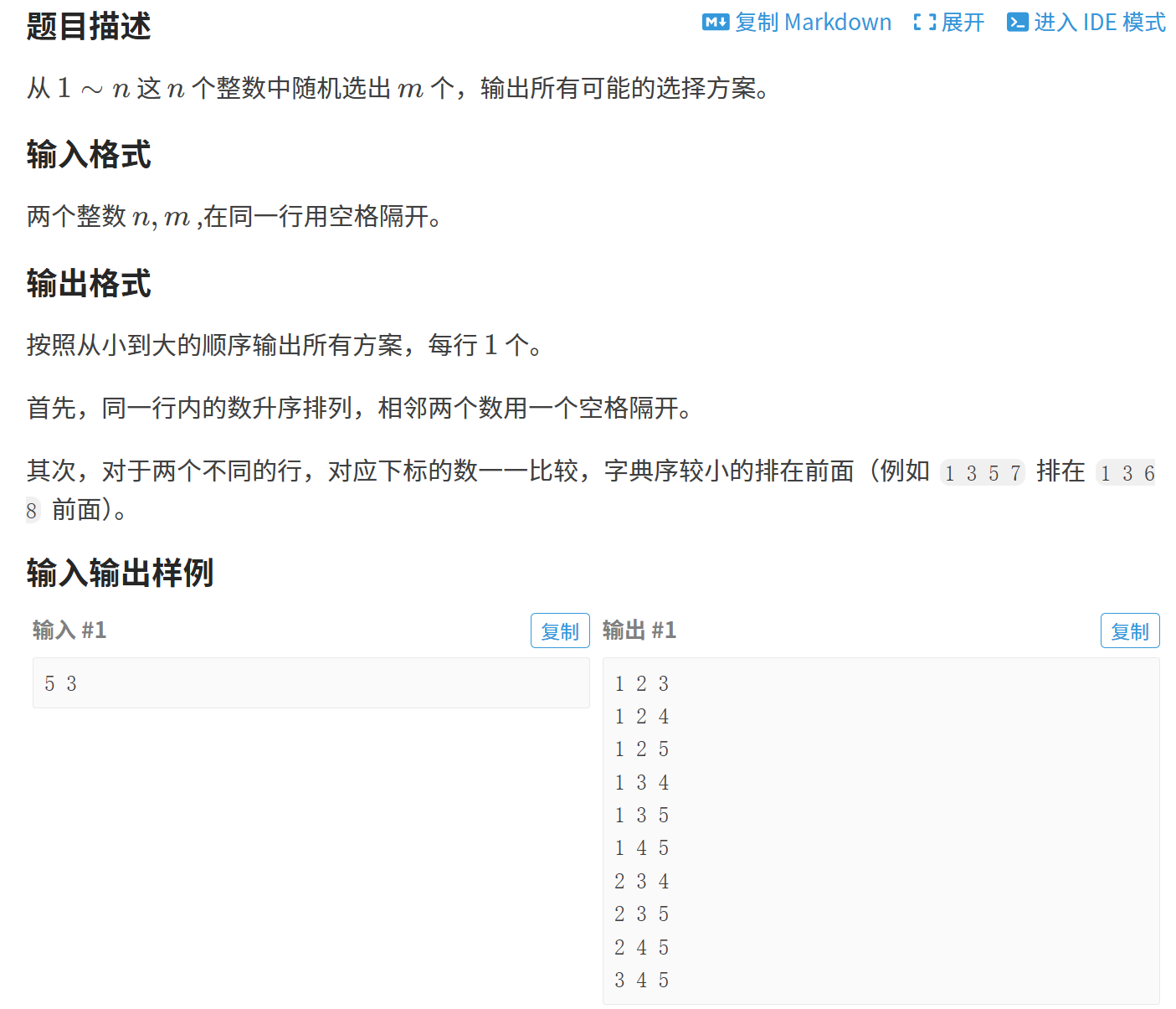
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, m;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(int begin)
{
if (path.size() == m)
{
for (auto e : path)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = begin;i <= n;i++)
{
path.push_back(i);
dfs(i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}1.3 枚举排列
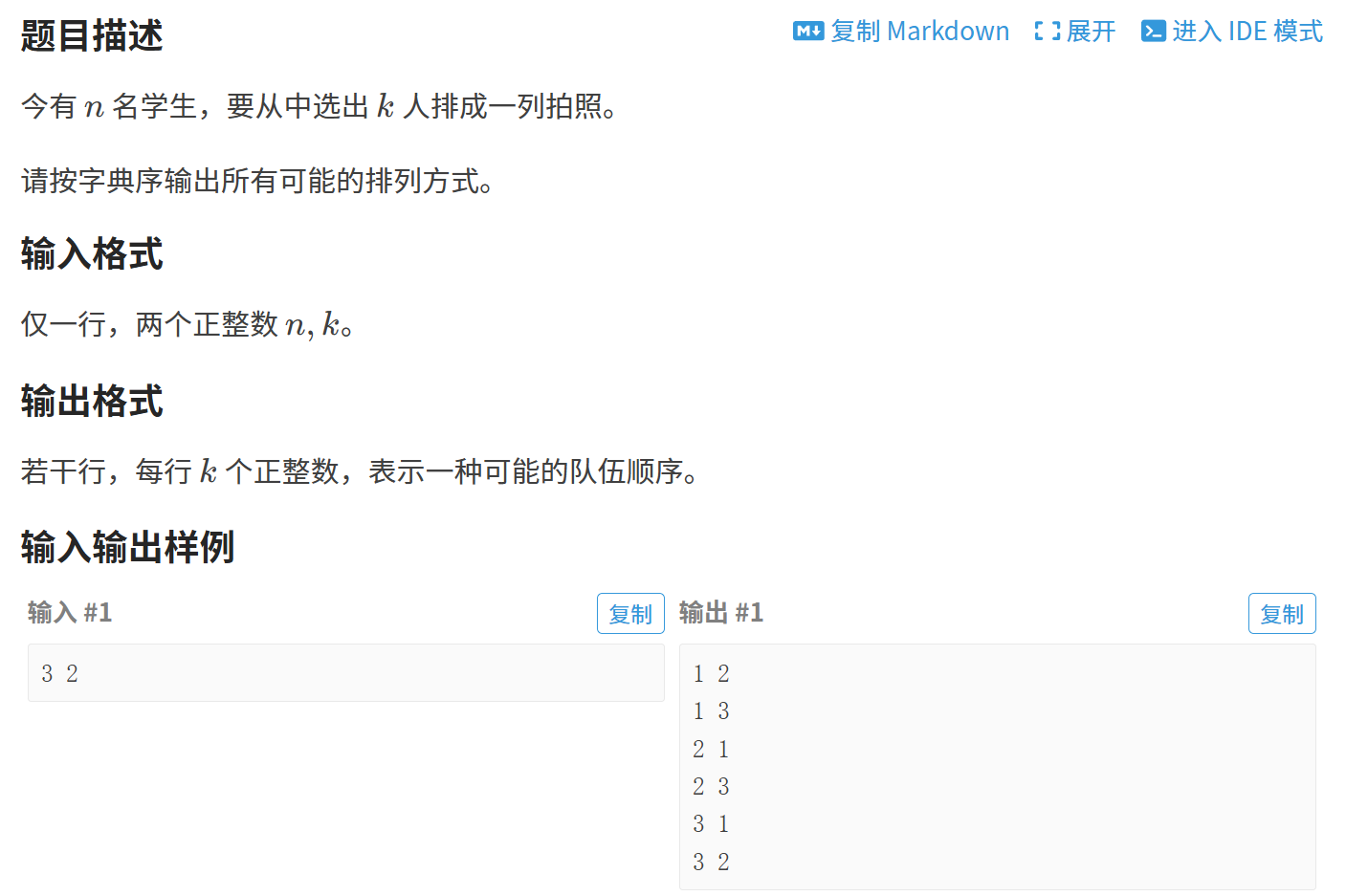
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n, k;
vector<int> path;
const int N = 20;
bool st[N];
void dfs()
{
if (path.size() == k)
{
for (auto e : path)
cout << e << " ";
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
if (st[i])
continue;
path.push_back(i);
st[i] = true;
dfs();
//恢复现场
st[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
dfs();
return 0;
}1.4 全排列

#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<int> path;
const int N = 10;
bool st[N];
void dfs()
{
if (path.size() == n)
{
for (auto e : path)
{
printf("%5d", e);
}
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
if (st[i])
continue;
path.push_back(i);
st[i] = true;
dfs();
path.pop_back();
st[i] = false;
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
dfs();
return 0;
}更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)